DIABETES SECONDARY SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS – Definition, types, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention
DIABETES SECONDARY SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS – Definition, types, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and prevention
Diabetes Secondary Symptoms
Definition:
Secondary symptoms of diabetes are complications or additional health issues that arise as a result of prolonged high blood sugar levels associated with diabetes mellitus. These symptoms can affect various organs and systems in the body.
Types:
Neuropathy (Nerve Damage):
Peripheral Neuropathy: Affects the extremities, causing pain, tingling, and numbness.
Autonomic Neuropathy: Affects autonomic nerves controlling internal organs, leading to digestive issues, bladder problems, and sexual dysfunction.
- Retinopathy (Eye Damage):
Diabetic Retinopathy: Damage to the blood vessels in the retina, potentially leading to blindness.
- Nephropathy (Kidney Damage):
Diabetic Nephropathy: Damage to the kidney’s filtering system, possibly resulting in kidney failure.
- Cardiovascular Disease:
Increased risk of heart attacks, strokes, and peripheral artery disease.
- Foot Complications:
Ulcers, infections, and in severe cases, amputations.
- Skin Conditions:
Bacterial and fungal infections, itching, and diabetic dermopathy.
Signs and Symptoms:
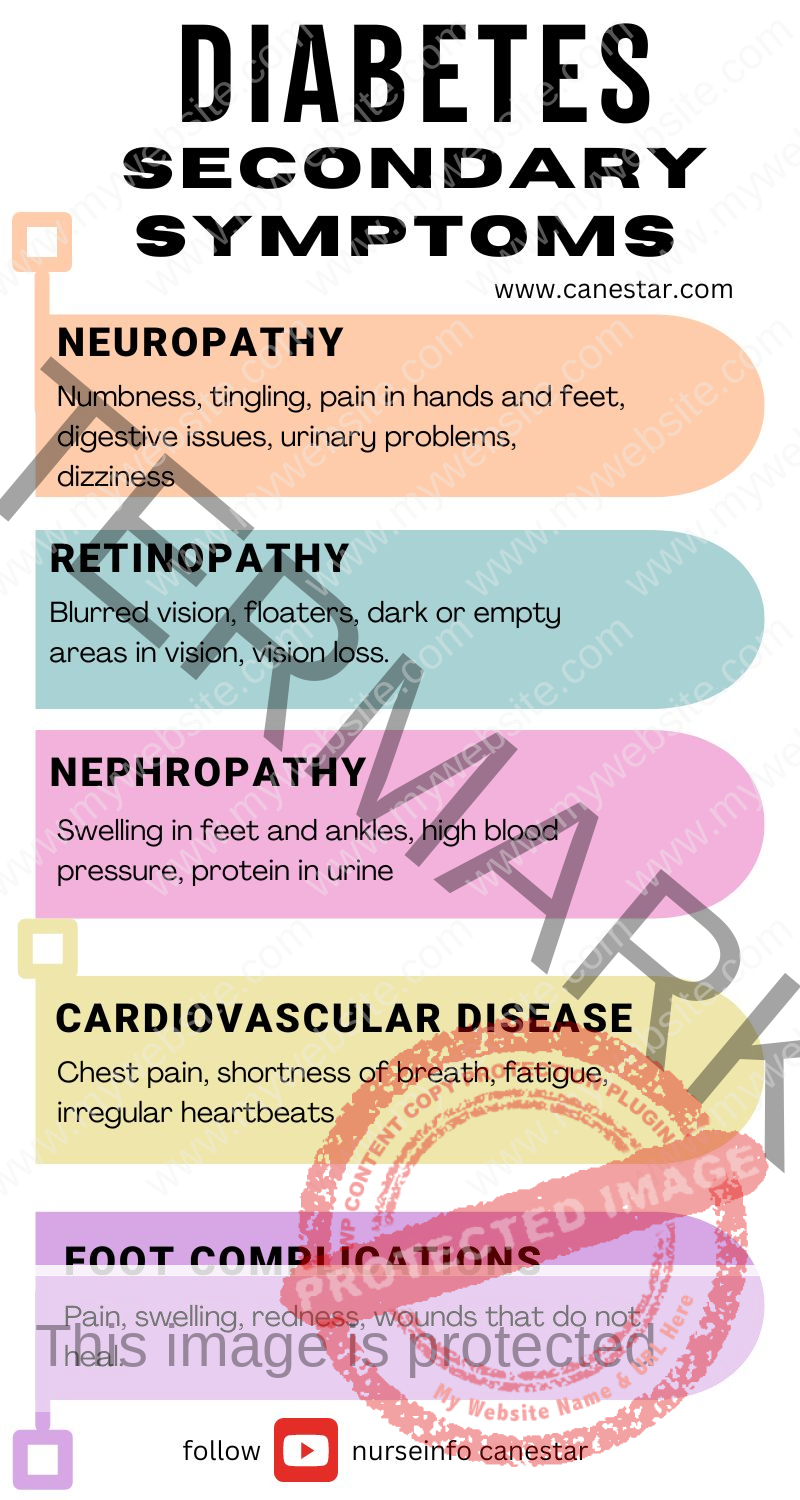
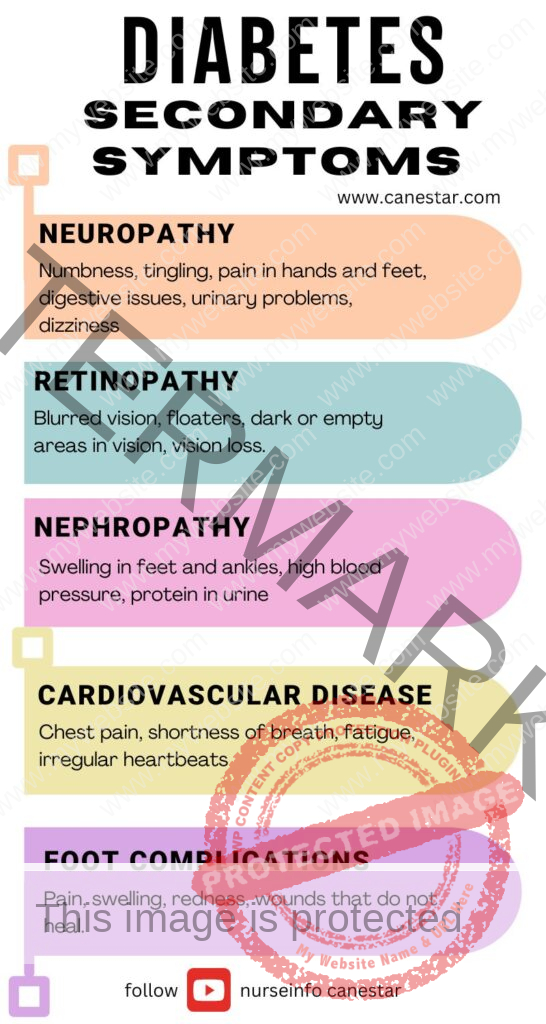
- Neuropathy: Numbness, tingling, pain in hands and feet, digestive issues, urinary problems, dizziness.
- Retinopathy: Blurred vision, floaters, dark or empty areas in vision, vision loss.
- Nephropathy: Swelling in feet and ankles, high blood pressure, protein in urine.
- Cardiovascular Disease: Chest pain, shortness of breath, fatigue, irregular heartbeats.
- Foot Complications: Pain, swelling, redness, wounds that do not heal.
- Skin Conditions: Itching, rashes, blisters, dryness.
Diagnosis:
- Blood Tests: HbA1c, fasting blood sugar, oral glucose tolerance test.
- Urine Tests: Check for protein (albumin) in the urine.
- Eye Exams: Dilated eye exam to check for retinopathy.
- Foot Exams: Regular check-ups for signs of nerve damage and poor circulation.
- Heart Tests: ECG, stress test, echocardiogram.
Treatment:
- Blood Sugar Control: Through medication (insulin or oral hypoglycemics) and lifestyle changes (diet and exercise).
- Medication for Complications:
Neuropathy: Pain relief medications, antidepressants, anti-seizure drugs.
Retinopathy: Laser therapy, injections.
Nephropathy: Blood pressure medications, ACE inhibitors, ARBs.
Cardiovascular Disease: Statins, aspirin, beta-blockers.
- Regular Monitoring: Frequent check-ups with healthcare providers.
- Foot Care: Proper foot hygiene, wearing comfortable shoes, regular foot exams.
Prevention:
- Healthy Diet: Balanced diet rich in vegetables, fruits, whole grains, lean proteins.
- Regular Exercise: At least 150 minutes of moderate aerobic activity per week.
- Blood Sugar Monitoring: Regularly checking blood sugar levels to ensure they are within target range.
- Avoid Smoking: Smoking cessation to reduce cardiovascular risk.
- Regular Medical Check-ups: Early detection and management of complications.
- Foot Care: Daily inspection of feet, maintaining good foot hygiene.
Effective management of diabetes and adherence to a healthy lifestyle can significantly reduce the risk and severity of secondary symptoms.
Disclaimer: This information is given for educational purpose. This information is provided for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute providing medical advice or professional services. The information provided should not be used for diagnosing or treating a health problem or disease, and those seeking personal medical advice should consult with a licensed physician. Always seek the advice of your doctor or other qualified health provider regarding a medical condition.