Excessive Heat – Heat Cramps, Heat Exhaustion and Heat Stroke – Definition, types, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
EXCESSIVE HEAT
Excessive Heat
Definition: Excessive heat refers to a condition where the body is exposed to high temperatures for a prolonged period, leading to heat-related illnesses. This occurs when the body cannot cool itself adequately, resulting in various health complications.
Types:
- Heat Cramps:
Involuntary muscle spasms, typically occurring in the legs or abdomen, due to electrolyte imbalances and dehydration.
- Heat Exhaustion:
A more severe form of heat illness characterized by heavy sweating, weakness, dizziness, nausea, and fainting.
- Heat Stroke:
The most severe form, a life-threatening condition where the body’s temperature regulation fails, leading to a body temperature of 104°F (40°C) or higher.
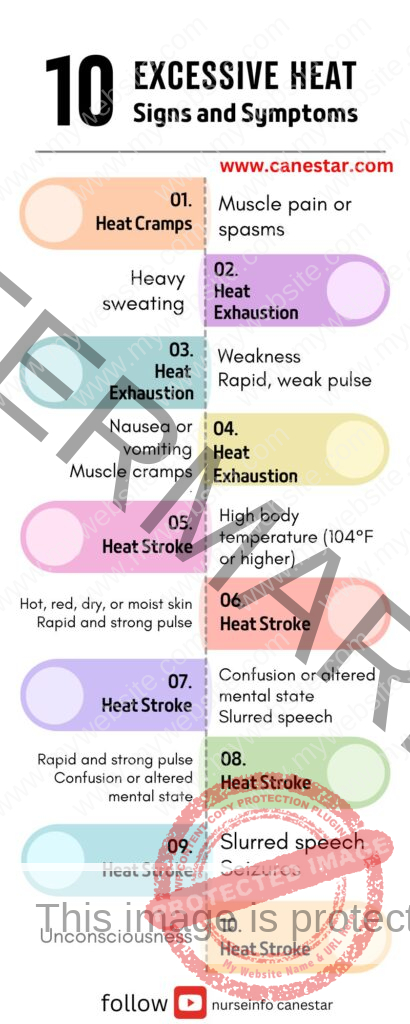
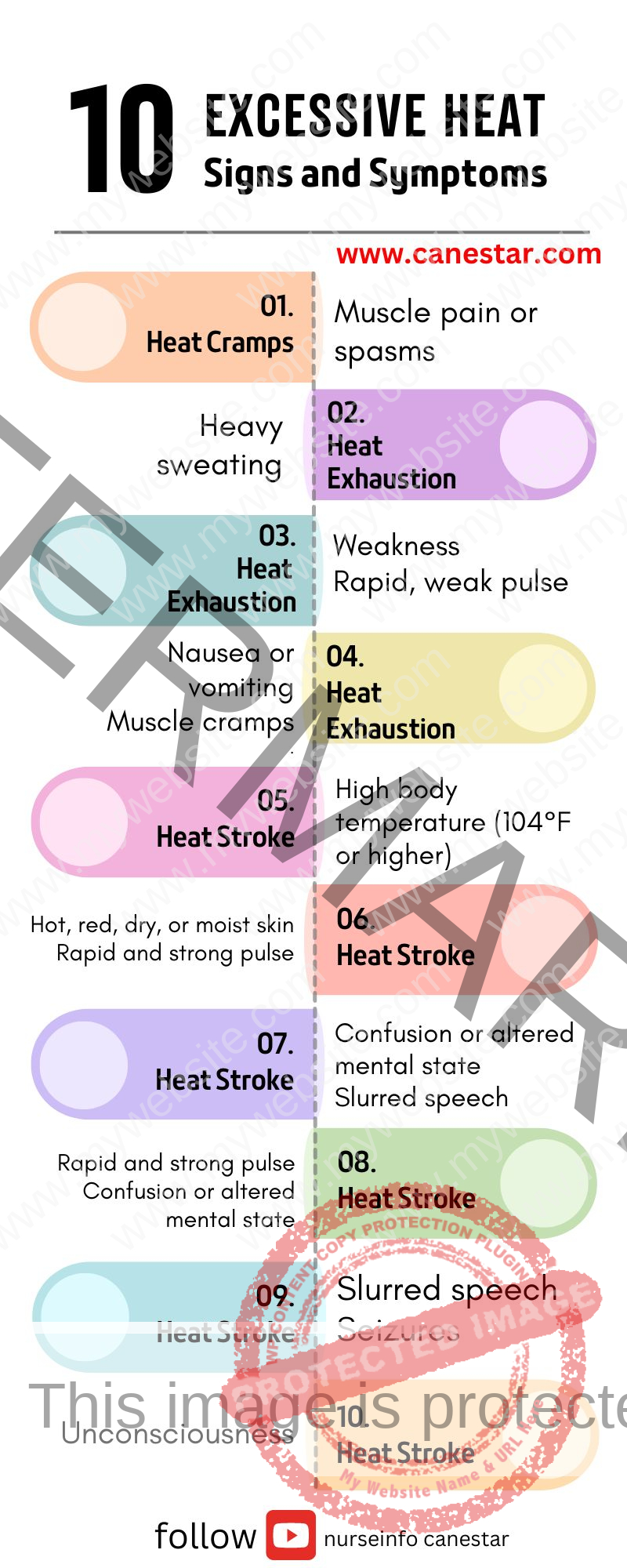
Signs and Symptoms:
- Heat Cramps:
Muscle pain or spasms, typically in the legs, arms, or abdomen.
- Heat Exhaustion:
Heavy sweating
Weakness
Cold, pale, and clammy skin
Rapid, weak pulse
Nausea or vomiting
Muscle cramps
Dizziness or fainting
Headache
- Heat Stroke:
High body temperature (104°F or higher)
Hot, red, dry, or moist skin
Rapid and strong pulse
Confusion or altered mental state
Slurred speech
Seizures
Unconsciousness
Diagnosis:
- Physical Examination:
Assessing the patient’s signs and symptoms.
Measuring body temperature.
- Laboratory Tests:
Blood tests to check for dehydration and electrolyte imbalances.
Urine tests to evaluate kidney function.
Treatment:
- Heat Cramps:
Move to a cooler place.
Drink water or sports drinks.
Stretch and gently massage affected muscles.
- Heat Exhaustion:
Move to a cool, shaded area.
Drink cool water or sports drinks.
Remove tight or unnecessary clothing.
Take a cool shower or bath.
Apply cool, wet cloths to the skin.
- Heat Stroke:
Seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Move to a cooler environment.
Reduce body temperature with cool cloths or a cool bath.
Do not give fluids if the person is unconscious or not alert.
Monitor breathing and be prepared to perform CPR if necessary.
Prevention Tips:
Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of fluids.
Wear lightweight, loose-fitting clothing.
Avoid strenuous activities during the hottest parts of the day.
Take frequent breaks in a cool or shaded area.
Use fans or air conditioning to stay cool.
Be aware of the signs of heat-related illnesses and take action promptly.