Hepatitis Definition, Causes and Sign and Symptoms
Hepatitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the liver. The inflammation can be acute (short-term) or chronic (long-term) and can lead to liver damage if left untreated. Hepatitis can result from various causes, including:
- Viral Infections: The most common cause, with several types of hepatitis viruses (A, B, C, D, E) known to infect the liver.
- Alcohol Abuse: Chronic alcohol consumption can lead to alcoholic hepatitis.
- Medications and Toxins: Certain drugs and toxins can cause liver inflammation.
- Autoimmune Diseases: The immune system mistakenly attacks liver cells.
- Other Infections: Infections such as mononucleosis or cytomegalovirus can also cause hepatitis.
Symptoms
Common symptoms of hepatitis include:
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dark urine
- Pale stool
- Joint pain
Diagnosis and Treatment
Hepatitis is diagnosed through blood tests, imaging studies, and sometimes liver biopsy. Treatment depends on the type and cause of hepatitis:
- Viral Hepatitis: Antiviral medications for types B and C.
- Alcoholic Hepatitis: Cessation of alcohol, supportive care.
- Drug-induced Hepatitis: Discontinuation of the offending drug, supportive care.
- Autoimmune Hepatitis: Immunosuppressive drugs.
Prevention
Preventative measures include vaccinations (for hepatitis A and B), safe practices to avoid bloodborne pathogens (for hepatitis B and C), maintaining good hygiene and sanitation (for hepatitis A and E), and avoiding excessive alcohol consumption.
HEPATITIS KEY INFORMATION
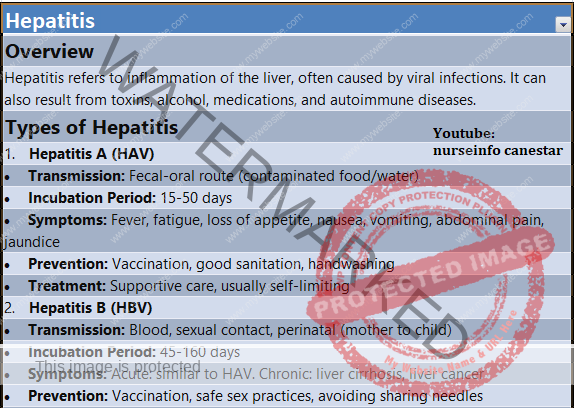
Overview
Hepatitis refers to inflammation of the liver, often caused by viral infections. It can also result from toxins, alcohol, medications, and autoimmune diseases.
Types of Hepatitis
Hepatitis A (HAV)
Transmission: Fecal-oral route (contaminated food/water)
Incubation Period: 15-50 days
Symptoms: Fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, jaundice
Prevention: Vaccination, good sanitation, handwashing
Treatment: Supportive care, usually self-limiting
Hepatitis B (HBV)
Transmission: Blood, sexual contact, perinatal (mother to child)
Incubation Period: 45-160 days
Symptoms: Acute: similar to HAV. Chronic: liver cirrhosis, liver cancer
Prevention: Vaccination, safe sex practices, avoiding sharing needles
Treatment: Antivirals for chronic HBV (e.g., tenofovir, entecavir)
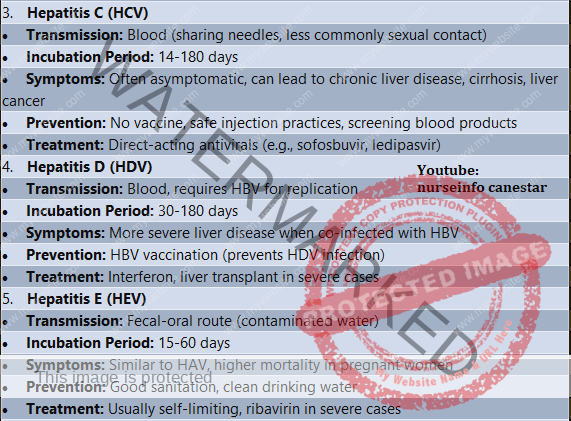
Hepatitis C (HCV)
Transmission: Blood (sharing needles, less commonly sexual contact)
Incubation Period: 14-180 days
Symptoms: Often asymptomatic, can lead to chronic liver disease, cirrhosis, liver cancer
Prevention: No vaccine, safe injection practices, screening blood products
Treatment: Direct-acting antivirals (e.g., sofosbuvir, ledipasvir)
Hepatitis D (HDV)
Transmission: Blood, requires HBV for replication
Incubation Period: 30-180 days
Symptoms: More severe liver disease when co-infected with HBV
Prevention: HBV vaccination (prevents HDV infection)
Treatment: Interferon, liver transplant in severe cases
Hepatitis E (HEV)
Transmission: Fecal-oral route (contaminated water)
Incubation Period: 15-60 days
Symptoms: Similar to HAV, higher mortality in pregnant women
Prevention: Good sanitation, clean drinking water
Treatment: Usually self-limiting, ribavirin in severe cases
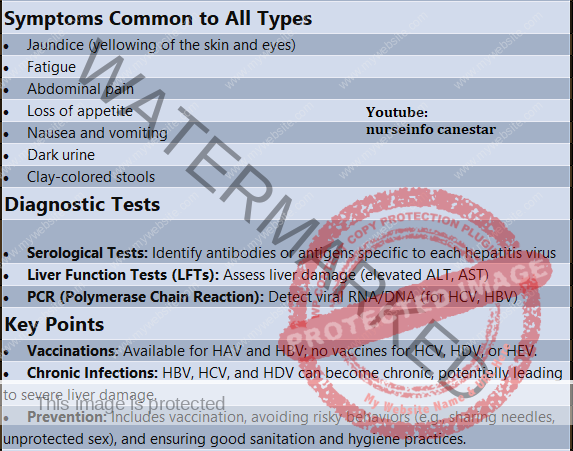
Symptoms Common to All Types
- Jaundice (yellowing of the skin and eyes)
- Fatigue
- Abdominal pain
- Loss of appetite
- Nausea and vomiting
- Dark urine
- Clay-colored stools
Diagnostic Tests
- Serological Tests: Identify antibodies or antigens specific to each hepatitis virus
- Liver Function Tests (LFTs): Assess liver damage (elevated ALT, AST)
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction): Detect viral RNA/DNA (for HCV, HBV)
Key Points
- Vaccinations: Available for HAV and HBV; no vaccines for HCV, HDV, or HEV.
- Chronic Infections: HBV, HCV, and HDV can become chronic, potentially leading to severe liver damage.
- Prevention: Includes vaccination, avoiding risky behaviors (e.g., sharing needles, unprotected sex), and ensuring good sanitation and hygiene practices.
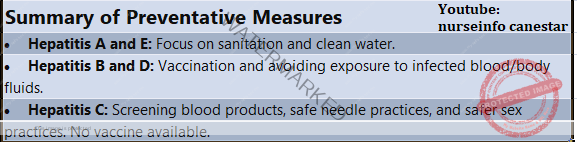
Summary of Preventative Measures
- Hepatitis A and E: Focus on sanitation and clean water.
- Hepatitis B and D: Vaccination and avoiding exposure to infected blood/body fluids.
- Hepatitis C: Screening blood products, safe needle practices, and safer sex practices. No vaccine available.
HEPATITIS MCQ WITH ANSWER
Question 1
Which of the following types of hepatitis is primarily transmitted through contaminated food and water? A) Hepatitis A
B) Hepatitis B
C) Hepatitis C
D) Hepatitis D
Answer: A) Hepatitis A
Question 2
Which hepatitis virus is most commonly associated with chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma? A) Hepatitis A
B) Hepatitis B
C) Hepatitis C
D) Hepatitis E
Answer: C) Hepatitis C
Question 3
Which of the following hepatitis viruses requires the presence of Hepatitis B virus (HBV) to replicate? A) Hepatitis A
B) Hepatitis B
C) Hepatitis C
D) Hepatitis D
Answer: D) Hepatitis D
Question 4
What is the most common route of transmission for Hepatitis B virus (HBV)? A) Fecal-oral route
B) Bloodborne route
C) Respiratory droplets
D) Vector-borne
Answer: B) Bloodborne route
Question 5
Which hepatitis virus has a vaccine available that is commonly given to children and healthcare workers? A) Hepatitis A
B) Hepatitis B
C) Hepatitis C
D) Hepatitis E
Answer: B) Hepatitis B
Question 6
Which of the following is a common symptom of acute hepatitis? A) Joint pain
B) Jaundice
C) Headache
D) Shortness of breath
Answer: B) Jaundice
Question 7
Which type of hepatitis is most commonly associated with waterborne outbreaks and is particularly concerning in pregnant women? A) Hepatitis A
B) Hepatitis B
C) Hepatitis C
D) Hepatitis E
Answer: D) Hepatitis E
Question 8
What is the primary mode of transmission for Hepatitis C virus (HCV)? A) Sexual contact
B) Contaminated food and water
C) Blood-to-blood contact
D) Respiratory droplets
Answer: C) Blood-to-blood contact
Question 9
Which laboratory test is used to confirm a diagnosis of Hepatitis B infection? A) Anti-HCV antibodies
B) HBsAg (Hepatitis B surface antigen)
C) Anti-HAV IgM
D) ALT (Alanine transaminase)
Answer: B) HBsAg (Hepatitis B surface antigen)
Question 10
Which of the following statements about Hepatitis E is true? A) It is primarily a chronic infection.
B) There is no vaccine available for it.
C) It can cause severe illness in pregnant women.
D) It is transmitted through sexual contact.
Answer: C) It can cause severe illness in pregnant women.
