HERPES STD SYMPTOMS – Definition, types, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
HERPES STD SYMPTOMS – Definition, types, signs and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Definition
Herpes is a viral infection caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV). It is categorized into two main types:
- HSV-1 (Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1): Typically causes oral herpes, which manifests as cold sores or fever blisters around the mouth and face.
- HSV-2 (Herpes Simplex Virus Type 2): Usually causes genital herpes, which affects the genital and anal areas.
Types
- Oral Herpes (HSV-1):
Causes cold sores or fever blisters on or around the mouth.
Can also cause sores inside the mouth (herpes stomatitis) or on the face.
- Genital Herpes (HSV-2):
Causes sores or blisters on or around the genital and anal areas.
Can be transmitted through sexual contact.
Signs and Symptoms
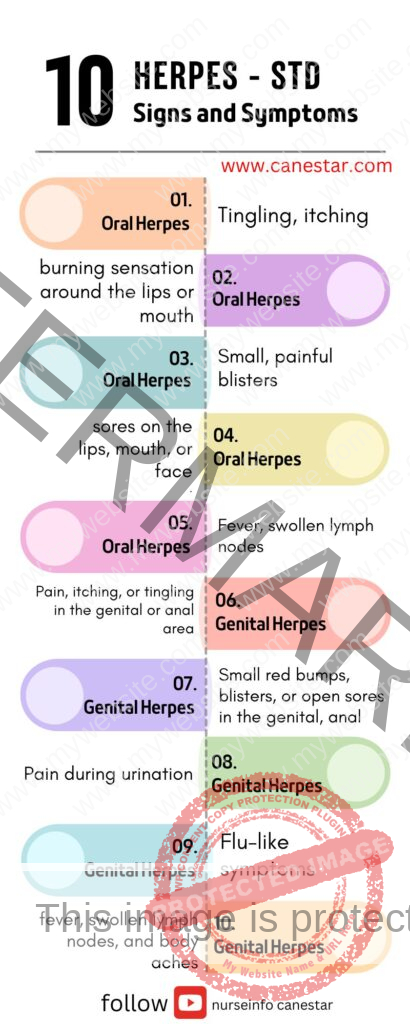
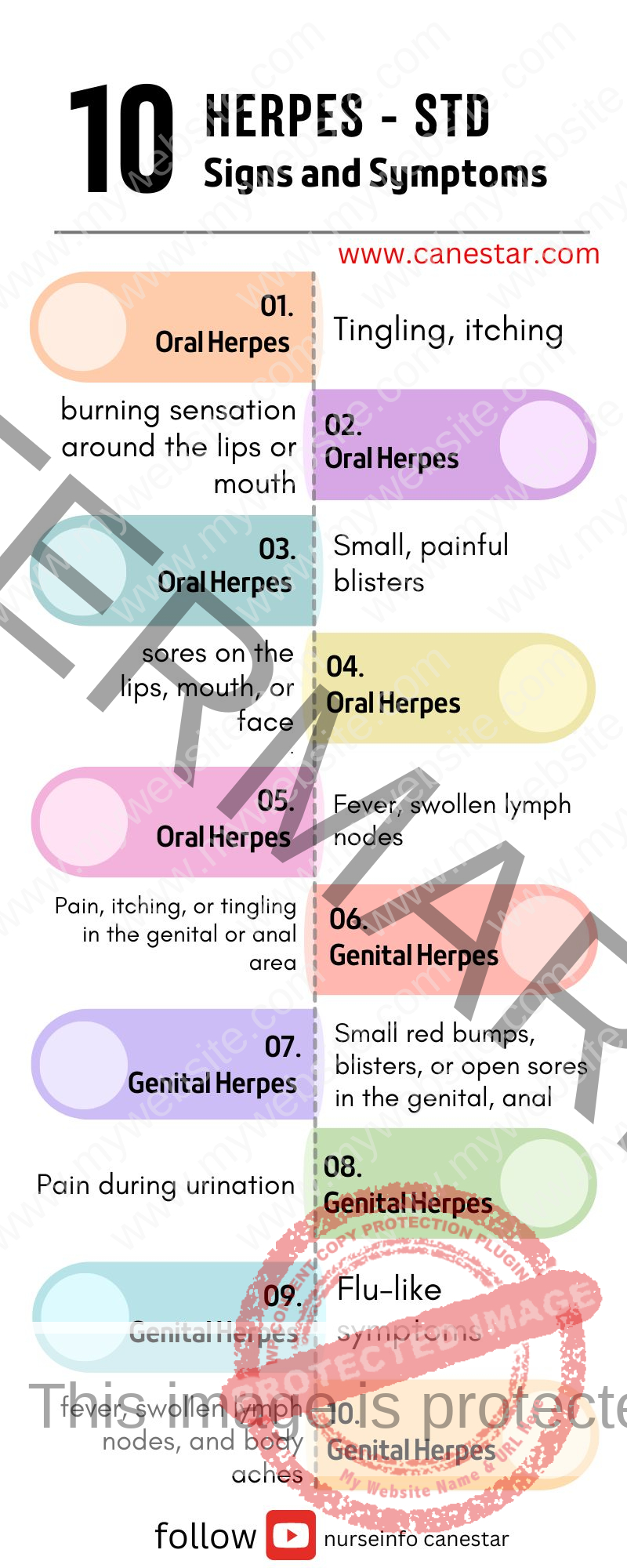
Oral Herpes (HSV-1):
- Tingling, itching, or burning sensation around the lips or mouth.
- Small, painful blisters or sores on the lips, mouth, or face.
- Fever, swollen lymph nodes, and sore throat in some cases.
- Difficulty swallowing if sores are inside the mouth.
Genital Herpes (HSV-2):
- Pain, itching, or tingling in the genital or anal area.
- Small red bumps, blisters, or open sores in the genital, anal, or nearby areas.
- Pain during urination.
- Flu-like symptoms, including fever, swollen lymph nodes, and body aches.
Diagnosis
- Physical Examination: Visual inspection of sores or blisters by a healthcare provider.
- Viral Culture: A sample from the sore is tested in a lab to detect the virus.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Test: Detects HSV DNA in blood, tissue, or sore samples.
- Blood Test: Detects antibodies to HSV-1 or HSV-2, indicating past or present infection.
Treatment
There is no cure for herpes, but treatment can help manage symptoms and reduce the risk of transmission:
- Antiviral Medications:
Acyclovir, Valacyclovir, and Famciclovir: These medications can help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms. They are used during outbreaks or as daily suppressive therapy.
- Pain Relief:
Over-the-counter pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help alleviate discomfort.
Topical anesthetics or antiviral creams may be applied to the sores to reduce pain and speed up healing.
- Self-care Measures:
Keep the affected area clean and dry.
Avoid touching sores to prevent spreading the virus to other parts of the body or to other people.
Avoid sexual contact during outbreaks and use condoms to reduce the risk of transmission.
Prevention:
- Avoid direct contact with sores or blisters.
- Use barrier protection methods (e.g., condoms) during sexual activity.
- Avoid sharing personal items like utensils, lip balm, or towels with someone who has an active herpes infection.
Herpes is a manageable condition with appropriate care and lifestyle adjustments. If you suspect you have herpes or experience symptoms, consult a healthcare provider for accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment.