Hot and Cold Application – Nursing procedure
Cold Compress:
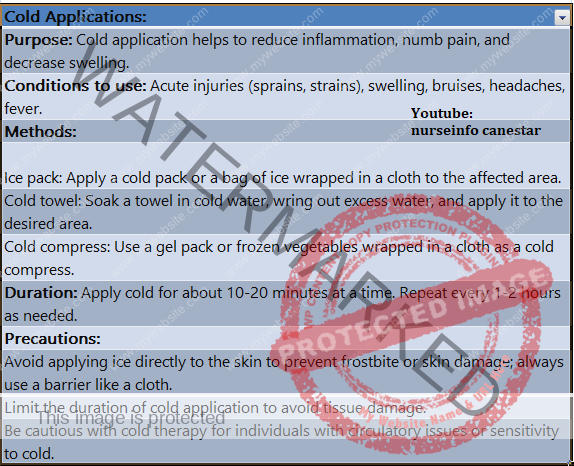
It is a local moist cold application. It may be sterile or unsterile. Sterile cold compresses are applied over open wounds or breaks in the skin. Cold compresses are made out of folded layers of gauze, lint piece or old soft linen, wring out of cold or ice water or in some evaporating lotion.
Article Required:
1. Large basin with ice.
2. Small basin with cold water.
3. Gauze pieces or small towels.
4. Waterproof pad.
5. Bath towel.
Procedure:
1. Explain the procedure to the client.
2. Wash hands.
3. Place the small basin with cold water into large basin with ice.
4. Place the compress in the cold water.
5. Keep the waterproof material under the part.
6. Check the area every 5 minutes.
7. Change the compress every 5 minutes or when it becomes hot.
8. Remove the compress after 20 minutes.
9. Put the area dry with a bath towel.
10. Make client comfortable.
11. Clean the equipment and place it in the proper place. Discard the used articles.
12. Wash hands
13. Document the care-time, site, duration of the application
Ice Cap:
Ice cap is a dry cold application. The ice cap used for the head, has a wide opening that allows it to be filled easily with ice chips, as does the ice collar, a narrow bag curved to fit the neck. Single use ice bags are frequently used.
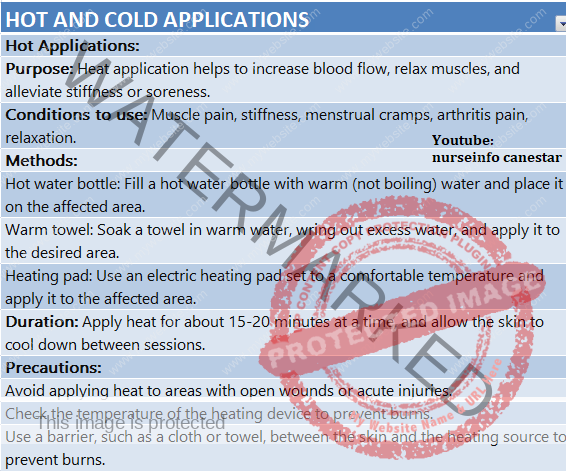
Hot Water Bag:
Hot water bags is also called hot water bottles, are rubber bags filled with hot water and used for heat therapy. It is used to manage pain, such as headache or arthritis, or keep yourself warm on a cold night. Hot water bottle are safer than electrical heating pads, which can start fires or cause electric shocks. Hot water bags may cause injury if we don’t use carefully.
Cold Sponging:
Cold sponging is used to reduce temperature in a client with hyperpyrexia. Large area of the body are sponged at one time permitting the heat of the body to transfer to the cooler solution on the body surface. Often wet towels are applied to the neck, axillae, groin and ankles where the blood circulation is close to the skin surface. Each area is dried by patting rather than by rubbing. Since the rubbing will increase the cell metabolism and raise the heat production. The vital signs are checked very frequently to detect the early signs of complications.
Cold sponging is hazardous to the client if the temperature of the body is brought down rapidly from a high temperature to a very low temperature. In cold sponging, the temperature of the water is kept between 65 and 90 degree F.
Tepid Sponging:
Tepid sponging is a safe method to reduce the body temperature in high pyrexia. It is carried out on the order of a physician. The temperature of the water is kept between 85 and 100 degree F.
Medical Fomentations: (Stupes)
Medical fomentations are moist heat applications, in which a medicine (e.g. turpentine) is applied locally to augment the effects of the hot compresses used. Stupes are commonly used to relieve tympanites by increasing the peristalsis and relaxing the muscle spasm.
Articles:
1. Kettle with boiling water.
2. Wringer with wringer rods placed in a basin.
3. Lint or flannel pieces, large enough to cover the area.
4. Plates (2)
A tray Containing:
1. Cotton balls in a container.
2. Forceps.
3. Olive oil or vaseline.
4. Paper bag.
5. Kidney tray.
6. Waterproof over and cotton pad.
7. Hot water bag with cover.
It will be necessary to insert a flatus tube to expel the flatus after the application of stupes.
The drugs used are:
Turpentine (1 part) well mixed with olive oil (3 parts) for adults. For children, turpentine (1 part) with olive oil (6 parts).
To apply the Turpentine Stupe:
Take the turpentine and the olive oil in the correct proportion, mix them well and warm it by keeping the container in a bowl of hot water. Apply the warm oil mixture over the part, apply the hot compresses and follow the procedure as in hot compresses. After 10 to 15 minutes, insert the flatus tube and watch the expulsion of the flatus.
Arm Soak and Foot Soak:
A soak refers to either immersing a body part (e.g. an arm, foot) in a solution or to wrap a part in gauze dressings and then saturating the dressing with a solution. Soaks may employ either “clean technique”. A sterile technique is indicated for any open wounds present on the area. Soaks are usually indicated for any one of the following reasons:
1. To apply heat, thus hastening suppuration and softening the exudates.
2. To apply medications.
3. To cleanse areas such as wound in which there are sloughing tissues.
4. To relieve oedema, ischaemia and muscle spasm.
The body parts to receive the moist heat application is submerged in a basin of warm water at 105 to 110 degree F. The duration of the treatment is usually 20 minutes. Ideally the temperature of the solution should be checked frequently and additional solution is added or the solution is replaced in order to maintain the appropriate temperature. The client should be in a comfortable position and the limbs are supported with pillows. Dry the surface throughly at the end of the treatment.
Infrared Rays: (Infrared Lamp)
Infrared lamps transmit infrared rays, which are visible heat rays beyond the red end of the spectrum.
Ultraviolet Rays: (Ultraviolet Lamp)
Ultraviolet lamps transmit infrared ray, which are invisible heat rays beyond the visible spectrum at the violet end.
Both these rays are used therapeutically for the production of heat in the tissues.
Therapeutic Uses:
1. Promotes healing of decubitus ulcer.
2. Softens connective tissue.
3. Relieves pain and spasm of the strained muscle.
The radiation heat produced by the infrared and ultraviolet lamps are more intense than the heat given off from the heating lamps. The effects of the exposure to the ultraviolet lamps are
1. Pigmentation of the skin.
2. Production of Vitamin-D.
3. Bacteriocidal effects.
The duration of the treatment is usually 20 to 30 minutes.
Precautions:
Observe the skin carefully during and after the treatment. The client and the therapist must use protective goggles during the treatment to shut out reflected harmful rays.
Sitz Bath (Hip Bath)
Sitz bath is a method of applying heat using tepid or hot water to the pelvic or rectal area by sitting in a tub. The client is usually immersed from the mid thigh to the iliac crest. The temperature of the water is 110-115 degree F and the duration of the bath is 15 to 30 minutes.
Purpose:
1. To relieve congestion of the pelvic organs e.g. in dysmenorrhoea.
2. To relieve pain following cystoscopy.
3. To reduce inflammation.
4. To promote drainage of rectal abscess and haemorrhoids.
Solutions Used:
1. Potassium permanganate solution 1:5000
2. Boric acid 1 dram to 1 pint.
3. Eusol solution.
Contraindications:
1. Pregnancy.
2. Menstruation.
3. Renal Inflammation.
4. Increased irritability of the genital organs.
Procedure:
1. Test the water in the bath tub with a thermometer before the client is allowed to enter into the water.
2. Assist the client to the tub or into the sitz bath and position properly.
3. Wrap a blanket around the shoulders to prevent exposure and chilling.
4. Monitor the client closely for sign of weakness and fatigue and discontinue the bath if faintness, pallor, rapid pulse or nausea occurs.
5. Check the temperature of the water in between and keep it at the desired temperature by adding hot water.
6. Do not leave the client alone in the bath tub.
7. When the bath is completed, assist the client to come out of the bath and dry well.
8. If the client complaints of fainting or weakness, assist him out of the bath.
9. The client may feel sleepy due to the sedative effect of the sitz bath, so care should be taken to prevent falling.
10. Record the procedure.
Steam Inhalation
Definition:
Inhalation of warm, moist air into the mucous membranes and respiratory tract.
Effects:
1. Relieves inflammation and congestion of the mucous membranes of the upper respiratory tract.
2. Relieves irritation (throat tickle) by moistening the air.
3. Loosens secretions and stimulates expectoration.
4. Relieves spasmodic breathing.
5. Relaxes muscles and thus relieves coughing.
6. Prevents excessive dryness of the mucous membranes.
Articles:
1. Boiling water in a kettle with spout.
2. Hot plate of gas stove or local stove using charcoal.
3. Vicks vaporub ointment or tincture Benzoin or camphor oil for good smelling secretion.
4. Old newspaper.
5. Umbrella
6. Sheets
7. Paper bag.
Procedure:
1. Fill kettle with water just below the level of the spout, and bring the water to boiling point. Add 1 tsp of medication (vicks or benzoin) into the boiling water.
2. Carry the stove and the kettle with caution near the bedside of the patient, if the patient is unable to stand or sit on the chair.
3. If croup tent is indicated, open an umbrella over the head of the patient and cover it with a sheet to form a tent.
4. With the newspaper make a cylindrical tube direct to the steam into the tent away from the patient’s face.
5. If the patient is able to sit on the chair, he may sit near the stove in the kitchen. With the cylindrical of paper the steam is directed into the patients face for inhalation.
6. Treatment time: 30 minutes to one hour, morning and evening, as tolerated.
Nebulization:
Nebulization is means of administering drugs by inhalation. Equalizer breaks up the solution to the inhaled into fine droplets which are then suspended in a stream of gas. The patient actively inhales this gas stream containing the drug.
Indications of Nebulization:
1. Delivery of bronchodilator drugs.
2. Infants and children with asthma.
3. Administration of antibiotics and antifungal agents.
4. To aid expectoration: inhalation of hypertonic saline has been found to increase clearance of bronchial secretions.
5. Local analgesia: to relieve dyspnoea in some terminally ill patients such as those suffering from alveolar carcinoma.
Types of Nebulizer:
1. Jet Nebulizer:
A high velocity of gas is blown through a fine hole creating an area of negative pressure.
Large Volume Nebulizer:
Used for long term therapy delivers heated or cool mist.
Side-stream Nebulizer:
It is attached to a ventilator or to an intermittent positive pressure breathing machine.
2. Ultrasonic Nebulizer:
High frequency sound waves are passed through a solution in a reservoir to create an aerosol. It is indicated for those in short therapeutic sessions. Indicated for the patient with thick secretions, to mobilize secretions and facilitate a productive cough.
Preparation of Articles:
1. Nebulizers
2. Pressurized gas source
3. Flow meter
4. Oxygen tubing
5. T-piece mouthpiece or mask
6. Sterile normal saline solution
7. 5 ml syringe and water
8. Prescribed medication
9. Suction equipment
10. Sputum mug
11. Kidney tray
12. Stethoscope
13. B.P apparatus, TPR tray.
Preparing Solution:
It is important to use a minimum of 3 ml of solution and preferably 4 ml in order to deliver an adequate percentage of the prescribed drug. (in an assessment of jet nebulizer when 2 ml was used only 50% of dose was released as aerosol whereas with volume of 4 ml 60-80%.
Procedure:
1. Explain procedure to patient.
2. Record patient’s vital signs to establishment a baseline.
3. Place patient in sitting or high fowlers position to facility lung expansion an aerosol dispersion.
4. Attach free end of the oxygen tubing to pressuized gas source.
5. Turn on the gas source and check outflow port, usually a and setting of 5-6 litres/min is adequate.
6. Instruct the patient to breathe slowly and evenly through his mouth.
7. After about 3 deep breaths he should breathe gently using his lower chest.
8. If possible, remain with the patient during treatment. (usually 15-20 minutes)
9. Take vital signs to detect adverse reactions to medications.
10. Encourage and assist the patient to cough and expectorate.
11. Briefly stop the treatment if he needs rest.
12. Instruct patient to report warmth discomfort or hot tubing.
13. Check water level frequently to prevent complications from inhaling drug hot air.
14. Make sure the patient is comfortable.
15. Provide a sputum mug for spiting the expectoration.
16. Record time date and duration of therapy type, amount of medication added to nebulizer.